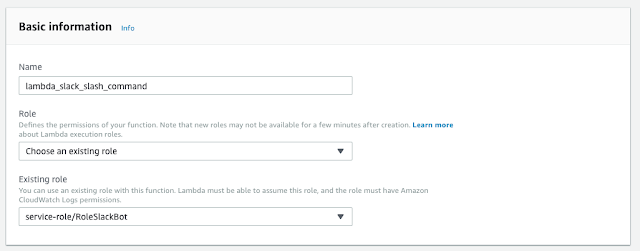
Install SAM CLI
$ sudo pip install --user --upgrade aws-sam-cli
Get a list of existing Lambda functions
aws lambda list-functions
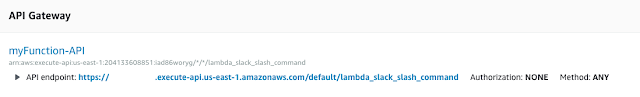
Using Postman to test AWS API Gateway
- download Postman app
$ sudo pip install --user --upgrade aws-sam-cli
aws lambda list-functions
$ sudo pip install --user --upgrade aws-sam-cli
aws lambda list-functions



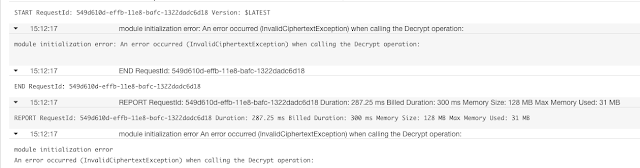
$ pip install jupyter_contrib_nbextensions
$ jupyter contrib nbextension install --user
$ jupyter notebook
$ pip install jupyter_contrib_nbextensions
$ jupyter contrib nbextension install --user
$ jupyter notebook
 Detroit Autonomous Vehicle and Robotics Meetup
Detroit Autonomous Vehicle and Robotics Meetup  Detroit Autonomous Vehicle and Robotics Meetup
Detroit Autonomous Vehicle and Robotics Meetup  The new LattePanda Alpha Single Board Computer has ample 8GB of RAM, operates on 12V, can run a MacOS with TuriCreate Machine Learning and use massive GPU connected via the M.2 bus, hence making it an excellent in-vehicle machine learning platform.
The new LattePanda Alpha Single Board Computer has ample 8GB of RAM, operates on 12V, can run a MacOS with TuriCreate Machine Learning and use massive GPU connected via the M.2 bus, hence making it an excellent in-vehicle machine learning platform.  The new LattePanda Alpha Single Board Computer has ample 8GB of RAM, operates on 12V, can run a MacOS with TuriCreate Machine Learning and use massive GPU connected via the M.2 bus, hence making it an excellent in-vehicle machine learning platform.
The new LattePanda Alpha Single Board Computer has ample 8GB of RAM, operates on 12V, can run a MacOS with TuriCreate Machine Learning and use massive GPU connected via the M.2 bus, hence making it an excellent in-vehicle machine learning platform. References:
https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04719
https://github.com/google/uis-rnn
https://catalog.ldc.upenn.edu/LDC2001S97
References:
https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04719
https://github.com/google/uis-rnn
https://catalog.ldc.upenn.edu/LDC2001S97
| Raspberry Pi 3B | 7-inch touchscreen | 7-inch case | 10.1 touchscreen | Infrared camera |
$ diskutil list
/dev/disk2 (external, physical):
#: TYPE NAME SIZE IDENTIFIER
0: FDisk_partition_scheme *15.9 GB disk2
1: Windows_FAT_32 PI3_RASBIAN 15.9 GB disk2s1
$ sudo diskutil unmountDisk /dev/disk2
Password:
Unmount of all volumes on disk2 was successful
$ sudo dd bs=1m if=/Users/uki/Downloads/2018-10-09-raspbian-stretch.img of=/dev/disk23944+0 records in3944+0 records out
4135583744 bytes transferred in 3019.441172 secs (1369652 bytes/sec)
$ sudo diskutil eject /dev/disk2Password:
Disk /dev/disk2 ejected
| Raspberry Pi 3B | 7-inch touchscreen | 7-inch case | 10.1 touchscreen | Infrared camera |
$ diskutil list
/dev/disk2 (external, physical):
#: TYPE NAME SIZE IDENTIFIER
0: FDisk_partition_scheme *15.9 GB disk2
1: Windows_FAT_32 PI3_RASBIAN 15.9 GB disk2s1
$ sudo diskutil unmountDisk /dev/disk2
Password:
Unmount of all volumes on disk2 was successful
$ sudo dd bs=1m if=/Users/uki/Downloads/2018-10-09-raspbian-stretch.img of=/dev/disk23944+0 records in3944+0 records out4135583744 bytes transferred in 3019.441172 secs (1369652 bytes/sec)
$ sudo diskutil eject /dev/disk2Password:Disk /dev/disk2 ejected